Do you hope to find 'ucmj article 92'? Here you can find all of the details.
Clause 92 of the Uniform Code of Military Justice (UCMJ) is "Failure to Obey an Guild or Regulation" (written or stated). The military considers IT a dereliction of duty when soldiers are unable surgery unwilling to do the job appointed to military force.
Table of contents
- Ucmj article 92 in 2021
- Ucmj article 134
- Ucmj article 92 punishment
- Article 92 ucmj for vaccination
- Universal code of military justice
- Article 92 covid
- Ucmj articles
- Manual for courts martial
Ucmj article 92 in 2021
 This picture shows ucmj article 92.
This picture shows ucmj article 92.
Ucmj article 134
 This picture shows Ucmj article 134.
This picture shows Ucmj article 134.
Ucmj article 92 punishment
 This picture demonstrates Ucmj article 92 punishment.
This picture demonstrates Ucmj article 92 punishment.
Article 92 ucmj for vaccination
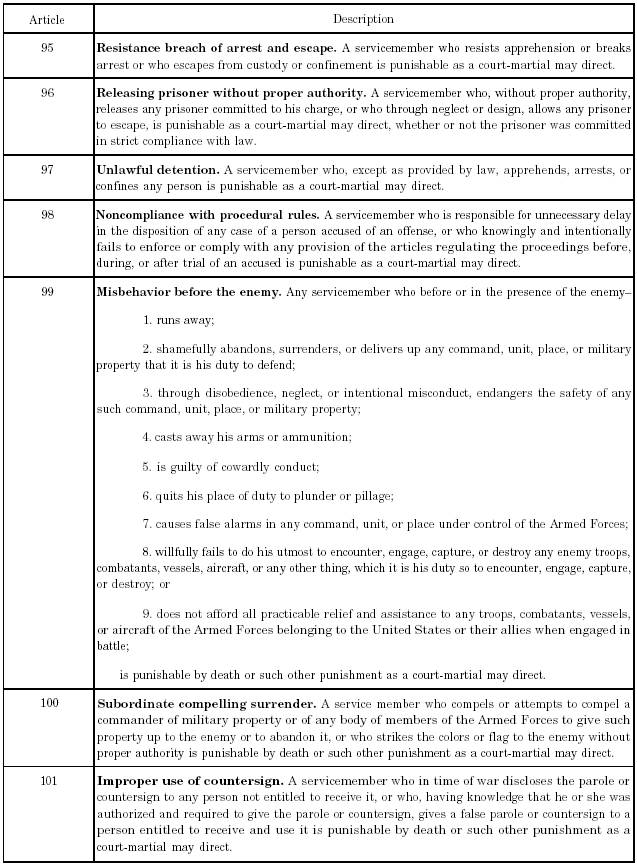 This picture illustrates Article 92 ucmj for vaccination.
This picture illustrates Article 92 ucmj for vaccination.
Universal code of military justice
 This image representes Universal code of military justice.
This image representes Universal code of military justice.
Article 92 covid
 This picture demonstrates Article 92 covid.
This picture demonstrates Article 92 covid.
Ucmj articles
 This image representes Ucmj articles.
This image representes Ucmj articles.
Manual for courts martial
 This image illustrates Manual for courts martial.
This image illustrates Manual for courts martial.
What happens if you violate Article 92 of the UCMJ?
The maximum possible punishment associated with violations of Article 92 depends upon the specifics of the violation itself. A violation of or failure to obey lawful general order or regulation may result in a dishonorable discharge, forfeiture of all pay and allowances, and confinement for 2 years.
Can a service member be prosecuted under Article 92?
The order or regulation must have been lawful and enforceable. A service member may be prosecuted under Article 92 for a violation of or failure to obey other lawful order if the order was lawful and the accused was aware of the order or regulation.
How is a violation of Article 92 prosecuted?
To be prosecuted for an Article 92 violation of failure to obey other lawful order, the prosecution must demonstrate: 1 that a member of the armed forces issued a certain lawful order; 2 that the accused had knowledge of the order; 3 that the accused had a duty to obey the order; and 4 that the accused failed to obey the order.
What are the different types of Article 92 offenses?
Article 92 creates three types of offenses - violations or failures to obey lawful general orders or regulations, failures to obey other lawful orders, and dereliction of duty. Article 92 charges are common in many prosecutions.
Last Update: Oct 2021